Spring into Better Hearing: Tips for Hearing Aid Users This Season
Welcome the Season with Clearer Sound As spring brings sunshine,
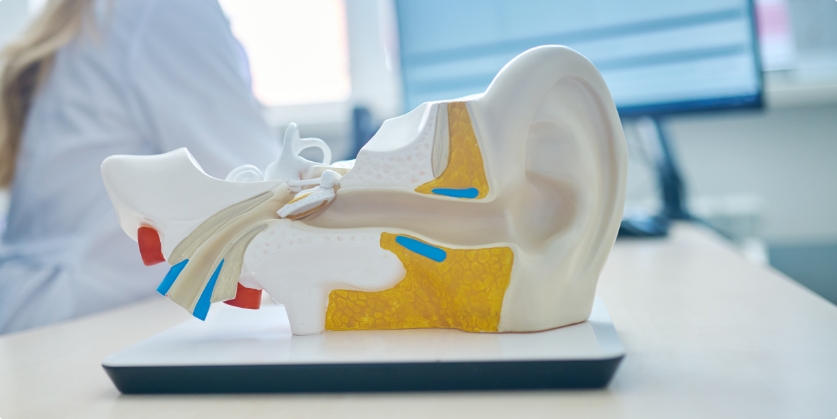
Tinnitus is the perception of sound when no actual external noise is present. Tinnitus can be described as ringing, buzzing, hissing, humming, swooshing or clicking. The Centers for Disease Control (CDC) estimates that tinnitus affects over 50 million Americans (about 15 to 20 percent of people in the general public). Tinnitus may be a symptom of an underlying condition, such as hearing loss, ear injury or a circulatory system disorder. Tinnitus can either be a temporary condition or a chronic (ongoing) condition, and ranges from mild (bothersome) to (extreme) debilitating.
There is currently no known cure for most types of tinnitus. There are, however, treatment options that can ease the perceived burden of tinnitus, allowing patients to live more comfortable, productive lives. With support from trained healthcare professionals, treatments can significantly reduce the perceived burden of tinnitus.
There are many claims about different products, treatments, services and dietary practices, and their impact on tinnitus. However, very few of these claims have been scientifically proven.
Evaluation for possible causes of tinnitus may include:
Possible treatments for tinnitus:
Medications
Drugs can't cure tinnitus, but in some cases they may help reduce the severity of symptoms or complications.

Welcome the Season with Clearer Sound As spring brings sunshine,
Adjustments you can make to your hearing aids by Oticon Companion app OR

Thanksgiving is a time for family, friends, and food, but for those with